CAT Scan:
- The term CAT stnads for "Computerized Axial Tomography" also called as CT Scan.
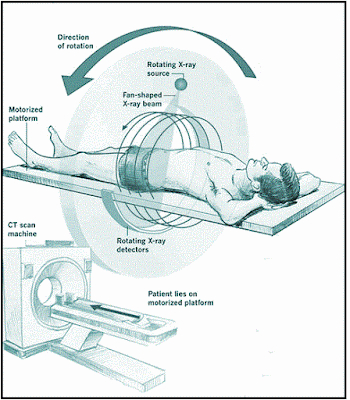
- It refers to a computerized X-ray imaging procedure in which a narrow beam of X-rays is aimed at a patient and quickly rotated around the body, producing signals that are processed by the machine’s computer to generate cross-sectional images or slices of the body.
- These slices are called tomographic images and contain more detailed information than conventional X-rays.
- Once a number of successive slices are collected by the machine’s computer, they can be digitally “stacked” together to form a three-dimensional image of the patient that allows for easier identification and location of basic structures as well as possible tumors or abnormalities.
- Unlike a conventional x-ray which uses a fixed X-ray tube, a CT scanner uses a motorized X-ray source that rotates around the circular opening of a donut-shaped structure called a gantry.
- During a CT scan, the patient lies on a bed that slowly moves through the gantry while the X-ray tube rotates around the patient, shooting narrow beams of X-rays through the body.
- Instead of film, CT scanners use special digital x-ray detectors, which are located directly opposite the X-ray source. As the X-rays leave the patient, they are picked up by the detectors and transmitted to a computer.
- Each time the X-ray source completes one full rotation, the CT computer uses sophisticated mathematical techniques to construct a 2D image slice of the patient.
- When a full slice is completed, the image is stored and the motorized bed is moved forward incrementally into the gantry.
- The X-ray scanning process is then repeated to produce another image slice. This process continues until the desired number of slices is collected.
- Image slices can either be displayed individually or stacked together by the computer to generate a 3D image of the patient that shows the skeleton, organs, and tissues as well as any abnormalities the physician is trying to identify.
- This method makes easier to find the exact place where a problem may be located and this method is also used to identify disease or injury within various regions of the body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of scan that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the inside of the body.
- An MRI scanner is a large tube that contains powerful magnets. You lie inside the tube during the scan.
- Most of the human body is made up of water molecules, which consist of hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
- At the center of each hydrogen atom is an even smaller particle, called a proton.. Protons are like tiny magnets and are very sensitive to magnetic fields.
- Most of the human body is made up of water molecules, which consist of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. At the center of each hydrogen atom is an even smaller particle, called a proton. Protons are like tiny magnets and are very sensitive to magnetic fields.
- Short bursts of radio waves are then sent to certain areas of the body, knocking the protons out of alignment. When the radio waves are turned off, the protons realign and this sends out radio signals, which are picked up by receivers.
- These signals provide information about the exact location of the protons in the body. They also help to distinguish between the various types of tissue in the body, because the protons in different types of tissue realign at different speeds and produce distinct signals.
- In the same way that millions of pixels on a computer screen can create complex pictures, the signals from the millions of protons in the body are combined to create a detailed image of the inside of the body.
CAT vs MRI Scan:
- Unlike CAT Scans, which use X-rays, MRI Scans use powerful magnetic fields and radio frequency pulses to produce detailed pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and other internal body structures. Differences between normal and abnormal tissue is often clearer on an MRI image than a CT.
- CAT Scan is good for seeing organs and bone details whereas MRI Scan is good for seeing soft tissue.
- MRI Scan takes longer time (30mins or more) than the CAT Scan (5-10mins)
 |
| CAT Scan vs MRI Scan |